A guide to glass wool, paper wool, stone wool and wood fiber for insulation
Insulation is a critical component of any construction project as it directly impacts the building's thermal performance and comfort. This makes the choice of insulation material a crucial decision. In this article, we will explore four popular insulation materials: glass wool, paper wool, rock wool and wood fiber. We will look at their advantages and disadvantages, the differences between them, their usefulness and other relevant aspects:


Lars Christiansen
Director of Isoleringsmaskinen A/S
22.09-2023
Glass wool
Glass wool is a type of insulating material made from molten glass which is then spun into fine fibres. These fibers are mixed with various binders and additives to create a lightweight but effective insulation material. Glass wool is known for its excellent thermal performance, sound insulation properties and fire safety. It is a popular choice for insulating buildings including homes, offices and industrial facilities.
Advantages of using insulation machines
Thermal Insulation: Glass wool has a low thermal conductivity, which makes it effective at keeping heat in in winter and out in summer.
Soundproofing: The porous fibers in glass wool help absorb sound waves, reducing noise levels inside.
Fire safety: Glass wool is non-combustible and therefore contributes to fire safety in buildings.
Moisture resistance: Although not completely water-resistant, glass wool can withstand a certain amount of moisture without losing its insulating effectiveness.
Environmentally friendly: Glass wool can be recycled and often contains a high percentage of recycled glass.
Lightweight: Its light weight makes it easy to install and handle, which can reduce labor costs.
Disadvantages
Irritation: The fibers can be irritating to the skin, eyes and respiratory tract, so it is important to take appropriate safety precautions during installation.
Moisture sensitivity: Although it is relatively moisture resistant, it may lose its effectiveness if it gets too wet.
Price: Quality glass wool can be more expensive than other insulation materials such as mineral wool or foam.
Application
Glass wool is used in a variety of insulation applications:
Ceiling insulation: It is commonly used in ceilings to prevent heat loss.
Wall insulation: It can be used in walls for both thermal and acoustic insulation.
Floor insulation: Although less common, it can also be used to insulate floors.
Pipe and ventilation insulation: It is also used to insulate heating and cold water pipes and ventilation ducts.
Industrial Applications: It is used in industrial processes where high temperature insulation is required.
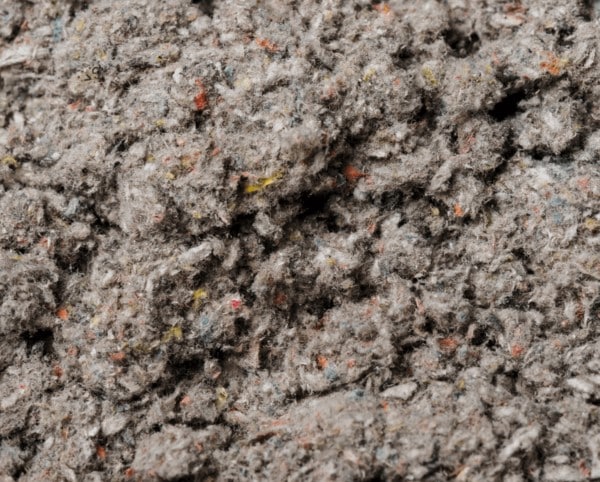

Paper wool
Paper wool is an insulation material made from recycled paper, often in the form of newspapers. This paper is treated with a number of chemical processes, including the addition of fire retardants and mould-resistant substances, to create a product suitable for insulation. Paper wool is known for its environmental friendliness, as it is primarily made from recycled materials, and it is also biodegradable.
Advantages of using insulation machines
Thermal Efficiency: Paper wool has good thermal insulation properties, making it effective at keeping heat inside a building in winter and outside in summer.
Sound insulation: Like glass wool, paper wool is also effective at dampening sound, making it a good choice for acoustic insulation.
Environmental friendliness: As it is primarily made from recycled paper, it is a sustainable resource that helps reduce waste.
Air quality: Paper wool is often free of harmful chemicals and can therefore contribute to better indoor air quality.
Applicability: It is easy to install as it can be sprayed into cavities or laid as batts.
Moisture regulation: Paper wool has some ability to absorb and release moisture, which can help regulate indoor humidity levels.
Disadvantages
Fire safety: Although treated with fire retardant chemicals, it is generally less fire resistant than mineral or glass wool.
Moisture sensitivity: It can be more sensitive to moisture compared to other insulation materials and may require a vapor barrier.
Price: It can be more expensive than other insulation materials, especially if it is of high quality or has special properties.
Installation: Although it is relatively easy to install, it still requires professional installation to ensure it is effective and safe.
Application
Ceiling insulation: It is a popular choice for insulating attics and roof spaces.
Wall insulation: It can be sprayed into wall cavities or laid as batts to provide thermal and acoustic insulation.
Floor insulation: Although less common, it can also be used in floors for additional insulation.
Specialized Applications: It can also be used in more specialized settings such as sound studios or theaters where acoustic insulation is particularly important.
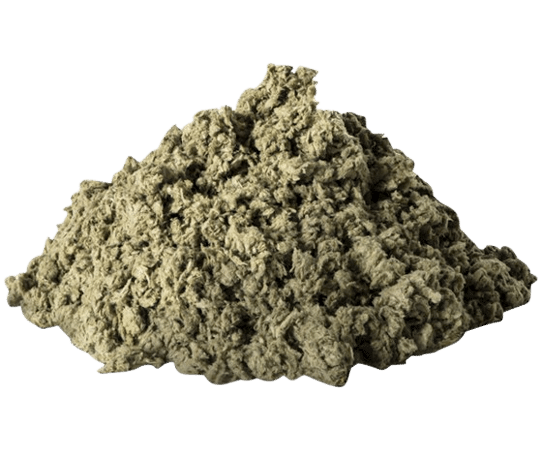

Stone wool
Rockwool, also known as rockwool or mineral wool, is an insulation material made from molten rock and minerals, which are then spun into fibres. These fibers are mixed with binders and other additives to create a robust and effective insulation material. Stone wool is known for its high thermal resistance, sound insulation properties and fire safety, making it a popular choice for many different types of construction projects.
Advantages of using insulation machines
Thermal Insulation: Rockwool has excellent thermal insulation properties, helping to keep buildings warm in winter and cool in summer.
Sound insulation: Its fibrous structure makes it effective at absorbing sound, reducing noise levels in buildings.
Fire safety: Stone wool is non-combustible and can withstand temperatures up to 1000°C, making it one of the most fire-resistant insulation materials on the market.
Moisture resistance: Rockwool is water-repellent and can resist moisture and mold, extending its life and efficiency.
Chemical Resistance: It is resistant to most chemicals and is therefore suitable for industrial applications.
Disadvantages
Irritation: The fibers in stone wool can be irritating to the skin and respiratory tract, so it is important to take appropriate safety precautions during installation.
Weight: It is generally heavier than other insulation materials such as glass wool or paper wool, which can make installation more difficult.
Price: It can be more expensive than other insulation materials, depending on the quality and specific characteristics.
Application
Ceiling insulation: It is commonly used in attics and roof spaces to prevent heat loss.
Wall insulation: It is also popular for insulating walls, both internal and external.
Floor insulation: It can be used in floors for additional thermal and acoustic insulation.
Pipe and ventilation insulation: It is also suitable for insulating hot and cold water pipes and ventilation ducts.
Industrial Applications: It is used in a number of industrial processes where high temperature insulation or chemical resistance is required.
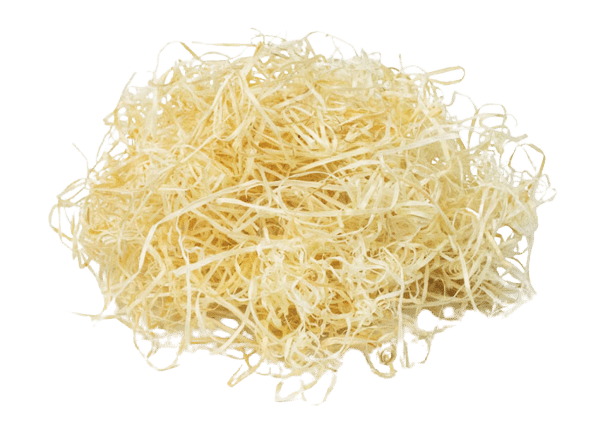

Wood wool
Wood fiber insulation is a natural insulation material made from wood fibers, often from sustainably managed forests. These wood fibers are processed and compressed into sheets, batts or loose fill materials that can be used in various insulation applications. Wood fiber insulation is known for its environmental friendliness, thermal performance and ability to improve indoor air quality.
Advantages of using insulation machines
Thermal Insulation: Wood fiber has good thermal insulation properties that help keep buildings warm in winter and cool in summer.
Sound insulation: Its natural structure makes it effective at absorbing sound, reducing noise levels in buildings.
Environmental friendliness: As it is made from natural and often recyclable materials, wood fiber is a sustainable and environmentally friendly insulation option.
Indoor climate: Wood fiber has the ability to regulate moisture, which can improve indoor air quality and create a healthier indoor climate.
Durability: It is a robust material that can withstand wear and tear over time, making it a long-term insulation solution.
Disadvantages
Fire safety: Although it can be treated to be more fire resistant, it is generally less fire resistant than mineral or stone wool.
Moisture sensitivity: It can be sensitive to moisture and may require a vapor barrier, especially in humid climates.
Price: High quality wood fiber insulation can be more expensive than synthetic alternatives.
Availability: It is not always as readily available as other more common insulation materials such as glass wool or stone wool.
Application
Ceiling insulation: It is suitable for insulating attics and roof spaces to minimize heat loss.
Wall insulation: It can be used in both interior and exterior walls for thermal and acoustic insulation.
Floor insulation: It is also effective for insulating floors, especially in combination with other insulating materials.
Specialized Applications: It can also be used in more specialized settings such as sound studios or in historic buildings where the use of natural materials is desirable.
“From an installer's perspective, there are several factors to consider when choosing the most appropriate insulation material for a given project. Here is a comparison of the four insulation types mentioned—glass wool, paper wool, stone wool and wood fiber—based on different criteria”
Installation efficiency
Glass wool: Lightweight and easy to break, making installation quick and simple. However, the fibers can be irritating to the skin and respiratory tract. Therefore, extra protection of the skin is recommended.
Paper wool: Can be injected into cavities, making it effective for irregular or hard-to-reach areas.
Stone wool: Heavier and more robust, which can make installation more difficult. However, has many advantages for industrial use.
Wood wool: Generally easy to work with, but has certain drawbacks and can be harder to obtain.
Fire safety
Glass wool: Non-flammable and contributes to fire safety.
Paper wool: Less fireproof, but very safe as it is treated with fire retardant chemicals.
Stone wool: Very fireproof, can withstand temperatures up to 1000°C.
Wood wool: Generally less fire resistant, but can be treated to improve fire safety.
Moisture resistance
Glass wool: Relatively moisture resistant, but may lose effectiveness if it gets too wet.
Paper wool: Sensitive to moisture and may require a vapor barrier.
Stone wool: Very moisture resistant and mold resistant.
Wood wool: Good for moisture regulation, but can be sensitive to high humidity.
Environmental impact
Glass wool: May contain recycled glass, but primarily made from new materials.
Paper wool: Very environmentally friendly as it is made from recycled paper.
Stone wool: Made from natural materials, but the process can be energy intensive.
Wood wool: Very environmentally friendly, especially if it comes from sustainably managed forests.
Recommendations for use
Glass wool: Best for projects where lightweight materials and quick installation are needed. Good for attic insulation and general construction projects.
Paper wool: Ideal for irregular or hard-to-reach areas and for those who want an environmentally friendly solution. Good for wall insulation.
Stone wool: Recommended for projects that require high fire safety and moisture resistance. Suitable for industrial applications and pipe insulation.
Wood wool: Best for those looking for a natural and sustainable solution. Good for use in historic buildings or in buildings where indoor air quality is a priority.
The choice of insulation material depends on a number of factors, including the project's specific needs, budget and environmental considerations. An installer must therefore assess all these aspects carefully in order to select the most suitable material.
Are you still in doubt about something?
Still stuck with a question? Then you are very welcome to contact us by phone: +45 31 36 62 86, or send an email to iso@isoleringsmaskinen.dk
You can also fill out our form by clicking the button below.
